Blown Film Extrusion Materials Used & Process
Blown Film Extrusion is an established process which is sued to manufacture a wide range of commodity & specialized plastic films for the packaging industry. Also known as Film Blowing Process, this extrusion process generally comprises extrusion of molten thermoplastic tube and its constant inflation to severaltimes of its initial diameter. This forms a thin, tubular product which may be used directly, or indirectly by slitting it to create a flat film.
Materials Used
In the process of Blown Film Extrusion, the common resins that are used are Polyethylenes (LDPE, HDPE and LLDPE). Though, various other materials can also be used in this process, as a blend with resins or even as single layers in the multi-layer film structure. Some of these materials are PP, PP, and EVOH. In few instances when these materials are not able to gel together, then a multi-layer film might get de-laminate. Hence, to overcome this issue, various tiny layers of special adhesive resins are used purposefully in between. These tiny layers are called “tie layers”.
Process of Blown Film Extrusion
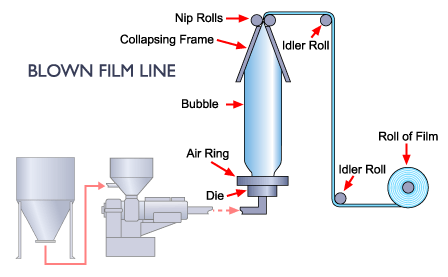
The extrusion of plastic melt is done via an annular slit die, generally vertically, for the formation of a thin walled tube. The introduction of air takes place through a hole present in the die's center for blowing up the tube just like a balloon. The cooling of the hot film is done by the high-speed air ring that blows onto it. This air ring is mounted on the top of die. Then following procedures take place:
- The tube of the film continues its movement upwards (constantly colling) till is is passed via nip rolls. Here, the tube is flattened for the creation of “lay-flat” tube of film. Also known as collapsed tube, this lay-flat tube goes back to the extrusion tower via rollers.
- On the higher output lines, exchange of air (which is available in the bubble) takes place. This is called IBS (Internal Bubble Cooling).
- Then the lay-flat film is kept as it is or its edges are slit off for producing 2 flat film sheets & wound up onto the reels. If kept as it is, the film's tube is created into bags by the process of sealing all across the film's width along with cutting or perforating. This process is carried out at a later stage or in line with the process of blown film.